The kinematic equations for objects experiencing free fall. The acceleration of free-falling objects is therefore called the acceleration due to gravity.
Suppose An Object Is In Free Fall Each Second The Object Falls - If you're searching for video and picture information linked to the key word you have come to visit the right site. Our website gives you hints for viewing the highest quality video and image content, hunt and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests. includes one of tens of thousands of movie collections from several sources, particularly Youtube, so we recommend this movie that you view. You can also contribute to supporting this site by sharing videos and graphics that you enjoy on this site on your social media accounts like Facebook and Instagram or tell your closest friends share your experiences concerning the simplicity of access to downloads and the information that you get on this website. This site is for them to stop by this site.
Free Fall With Air Resistance Terminal Velocity Youtube
Without the effect of air resistance each object in free fall would keep accelerating by 980665 ms approximately equal to 3217405 fts every second.

Suppose an object is in free fall each second the object falls. Objects that are said to be undergoing free fall are not encountering a significant force of air resistance. Then well look at both dimensions simultaneously. The acceleration due to gravity is constant which means we can apply the kinematics equations to any falling object where air resistance and friction are negligible.
An object that is moving vertically through the air with no physical constraints on its motion is said to be in free fall. B The object is gaining an equal amount of momentum for each meter it falls. This means that if the object is dropped we know the initial velocity is zero.
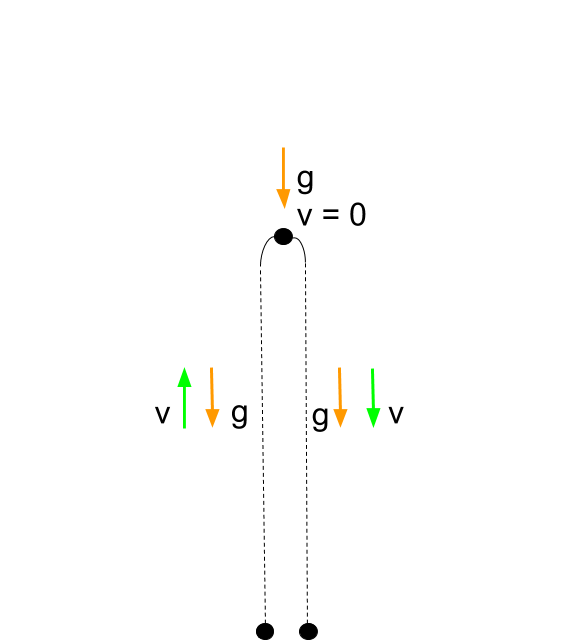
The force of gravity causes objects to fall toward the center of Earth. A ball is launched horizontally in and hits the ground in 8 seconds. The dot diagram at the right depicts the acceleration of a free-falling object.
As learned in an earlier unit free fall is a special type of motion in which the only force acting upon an object is gravity. A The object is gaining an equal amount of momentum for each second it is in free fall. G is the free fall acceleration expressed in ms² or fts².
The acceleration due to gravity is constant which means we can apply the kinematics equations to any falling object where air resistance and friction are negligible. An object that is moving only because of the action of gravity is said to be free falling and its motion is described by Newtons second law of motion. Free Falling Object Motion An object that falls through a vacuum is subjected to only one external force the gravitational force expressed as the weight of the object.
If it had been launched with a much higher speed in the same direction it would have hit the ground in. An object is in freefall on Earth. The force of gravity causes objects to fall toward the center of Earth.
C The object is gaining an equal amount of kinetic energy for each meter it falls. Once the object is in motion the object is in free-fall. The position of the object at regular time intervals - say every 01 second - is shown.
Each second the object falls athe same distance as in the second before bwith the same average speed ca larger distance than in the second before dwith the same instantaneous speed enone of the above. The fact that the distance that the object travels every interval of time is increasing is a sure sign that the ball is speeding up as it falls downward. They are falling under the sole influence of gravity.
Free Falling Objects So far we have only looked at objects moving in a horizontal dimension. Under these circumstances the motion is one-dimensional and has constant acceleration latextextglatex. In reality though a falling objects velocity is.
Today well look at objects moving in the vertical. The acceleration of free-falling objects is therefore called the acceleration due to gravity. Which of the following statements is true.
Suppose an object is in free fall. For every second the object travels 98m When the object is at two seconds the distance travelled is gravity x time -- 98 x 2 196ms2 Finding the increase is.
Falling In Air
Speed Velocity And Acceleration Ppt Download
Free Fall Definition Movement Under The Force Of Gravity Only Ppt Download
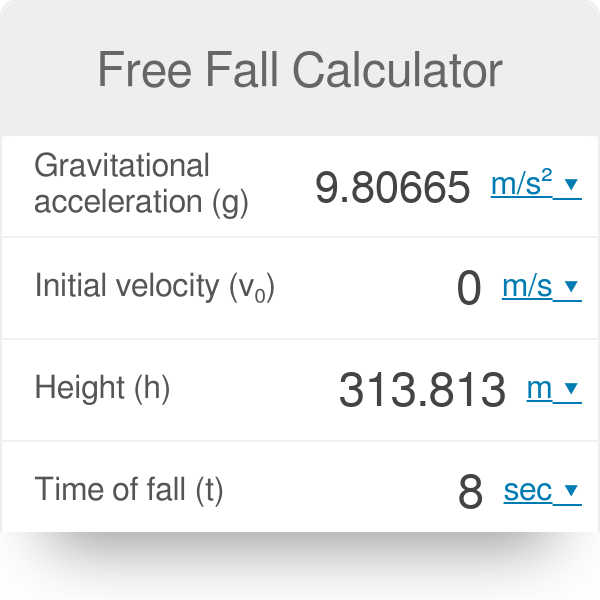
Free Fall Calculator
Speed Velocity And Acceleration Ppt Download
How To Solve A Free Fall Problem Simple Example Youtube
Assignment Answers Chapter 2
Speed Velocity And Acceleration Ppt Download
Freefall Review Article Khan Academy