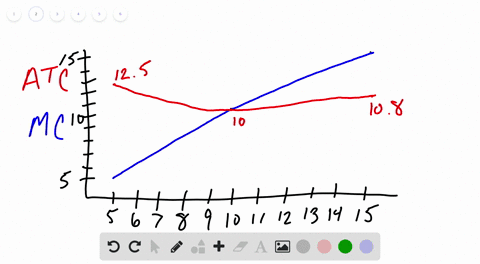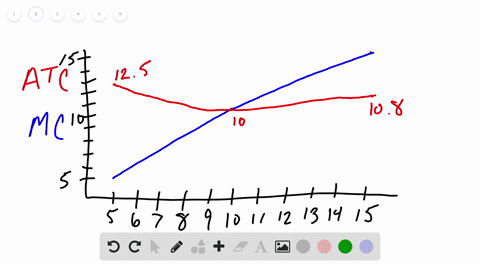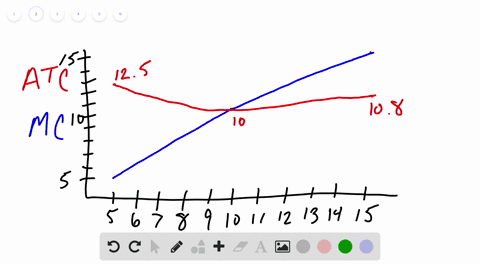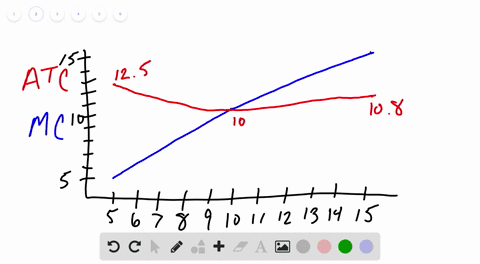
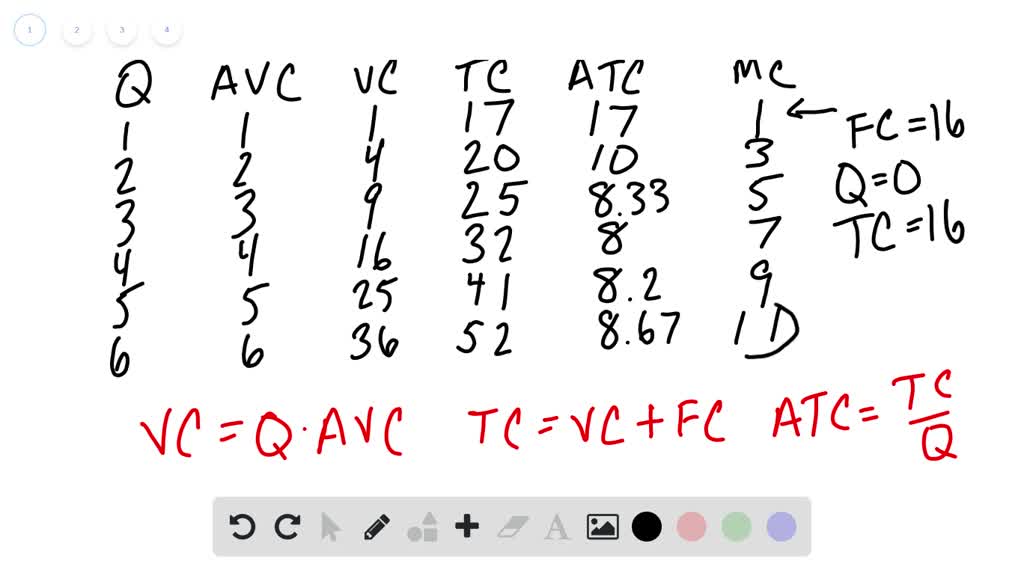
Other things equal if the prices of a firms variable inputs were to fall. Average variable cost would fall but marginal cost would be unchanged.
Other Things Equal If The Prices Of A Firms Variable Inputs Were To Fall - If you're looking for picture and video information linked to the key word you've come to pay a visit to the right site. Our website provides you with hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, search and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests. comprises one of tens of thousands of video collections from various sources, especially Youtube, so we recommend this movie for you to see. It is also possible to contribute to supporting this website by sharing videos and graphics that you enjoy on this blog on your social networking accounts like Facebook and Instagram or tell your closest friends share your experiences concerning the ease of access to downloads and the information you get on this site. This blog is for them to visit this site.
Https Canvas Uw Edu Files 45416261 Download Download Frd 1
The fall in the wage rate has a substitution effect an output effect and a profit-maximising effect as in the case of a perfectly competitive firm.
Other things equal if the prices of a firms variable inputs were to fall. Marginal cost average variable cost and average fixed cost would all fall. Marginal cost average variable cost and average total cost would all fall. These curves are also known as outlay lines price lines input-price lines factor-cost lines constant-outlay lines etc.
Other things equal if the prices of a firms variable inputs were to fall. A one could not predict how unit costs of production would be affected. Profits in short run number of firms in the industry in the long run A supernormal decrease B supernormal increase C normal remain the same D subnormal decrease 6 When a firm doubles its variable inputs its fixed inputs are unchanged and output less than doubles.
Not all supply curves slope upwards. The equilibrium price rises. Other things equal if the prices of a firms variable inputs were to fall.
Answer one could not predict how unit costs of production would be affected. However other things do not remain equal. The law of supply dictates that all other things remaining equal an increase in the price of the good in question results in an increase in quantity supplied.
Other things equal if the prices of a firms variable inputs were to fall. The result is that the equilibrium price stays the same as quantity sold increases. A one could not predict how unit costs of production would be affected.
Ceteris paribus means other things being equal When we draw a demand or supply curve we show the relationship between quantity demanded or quantity supplied and price and hold all other factors which might affect demand or supply other than price constant. However there are exceptions to the law of supply. Depending on precisely how they seek to.
Goods and services are produced using combinations of labor materials and machinery or what we call inputs also called factors of production. Marginal cost average variable cost and average fixed cost would all fall. But other things are never equal.
We are now going to continue our discussion of factor markets and were going to go beyond just thinking about labor as a factor in fact in this video well are going to start thinking about capital as well which we know is another one of the factors of production but just as a little bit of review weve already thought about it from a firms perspective on what is the rational amount of Labor to hire based on the. In a demand increased and supply met it. C marginal cost average variable cost and.
Some inputs were scarce or wages were rising. Other things equal if. If a firm faces lower costs of production while the prices for the good or service the firm produces remain unchanged a firms profits go up.
In other words the supply curve slopes upwards. Marginal cost average variable cost and average total cost would all fall. Having studied the nature of isoquants which represent the output possibilities of a firm from a given combination of two inputs we pass on to the prices of the inputs as represented on the isoquant map by the isocost curves.
Average variable cost would fall but marginal cost would be unchanged. B marginal cost average variable cost and average fixed cost would all fall. A one could not predict how unit costs of production would be affected.
If the price elasticity of demand for a firms output is unit elastic then marginal revenue is equal to zero and total revenue is at a maximum. Other things equal if the prices of a firms variable inputs were to fall. In b notice that sellers were not able to increase supply as much as demand.
5 5 pts Question 10 Diseconomies of scale arise primarily because. The production function describes a boundary or frontier representing the limit of output obtainable from each feasible combination of inputs. Firms invariably respond to new taxes in order to minimise their costs.
Notice that the supply increase is equal to the demand increase. If the wage rate falls to w 2 the firm would move along its MRP L curve to point A if other things remained equal. Of the difficulties involved in managing and coordinating a large business enterprise.
Marginal cost average variable cost and average total cost would all fall. B marginal cost average variable cost and. One could not predict how unit costs of production would be affected.
Other things equal if the prices of a firms variable inputs were to fall. Firms use the production function to determine how much output they should produce given the price of a good and what combination of inputs they should use to produce given the price of capital and labor. One could not predict how unit costs of production would be affected.
Question 9 Other things equal if the prices of a firms variable inputs were to fall. Price cost O output MC AC AR MR What is the correct analysis of this position.
Solved An Industry Currently Has 100 Firms Each
Short Run Supply
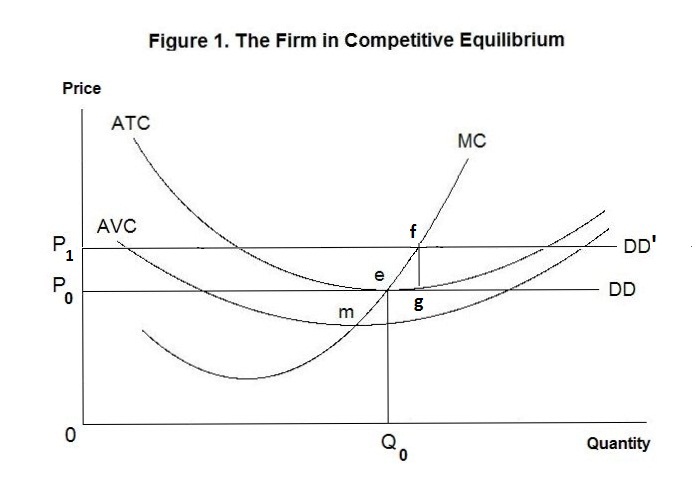
The Firm Under Competition And Monopoly
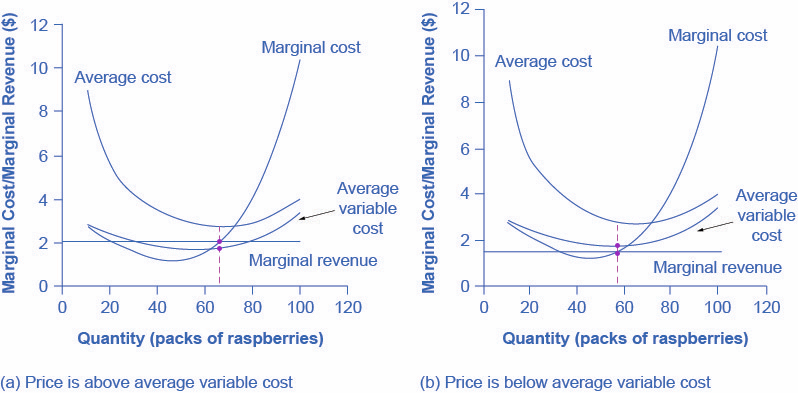
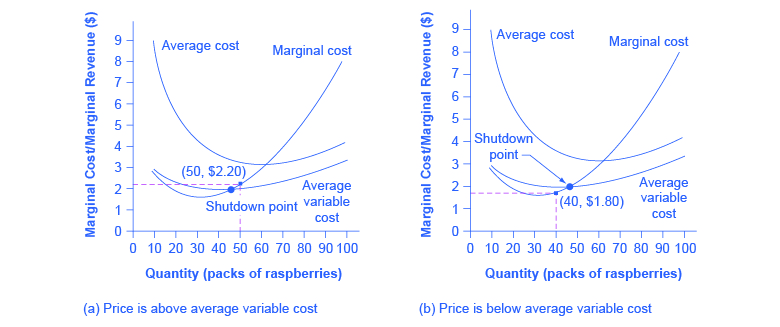
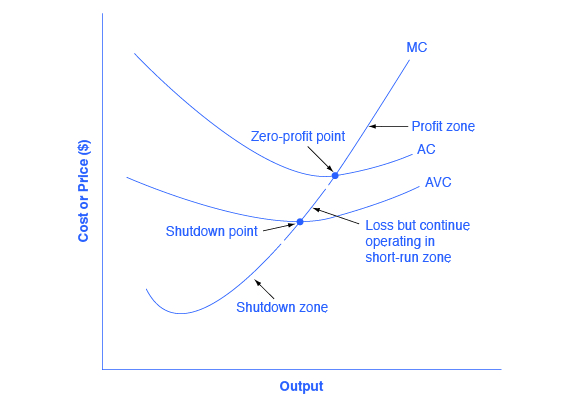
The Shutdown Point Microeconomics
Reading The Shutdown Point Microeconomics
Reading The Shutdown Point Microeconomics
Firm Production And Costs
Pin By The Radiance Room On Intermediate Microeconomics How To Run Longer Total Cost False
Solved An Industry Currently Has 100 Firms Each